WASTE ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC EQUIPMENT

We interacted with over 4 million Romanians during our activity. We listened to their opinions and questions and here is a summary of the most relevant things about WEEE, to help you understand what they are, what they contain and why it's good to collect and recycle them, as well as where you can hand over them.
What's WEEE?

WEEE means all electrical and electronic equipment obsolete that worked with the help of batteries or based on electricity: refrigerator, iron, washing machine, TVs, computers, mobile phones, radio cassette players, video cameras, microwave ovens, etc. Basically, they are all around you and significantly contribute to your life quality.
You have certainly changed a few that have become obsolete or damaged. Can you recall what you did with them? At this time, e-waste represents 5% of the world's total waste solid municipal packaging, almost the same amount as all plastic packaging, but WEEE is much more dangerous.
Why hand over and recycle WEEE?
There are two very important reasons:
- WEEE contains substances that are dangerous for the environment and our health - greenhouse gases or heavy metals harmful to health.
- Recovery of significant quantities of secondary raw materials; WEEE has a high degree of recycling-reuse (between 85-90%)

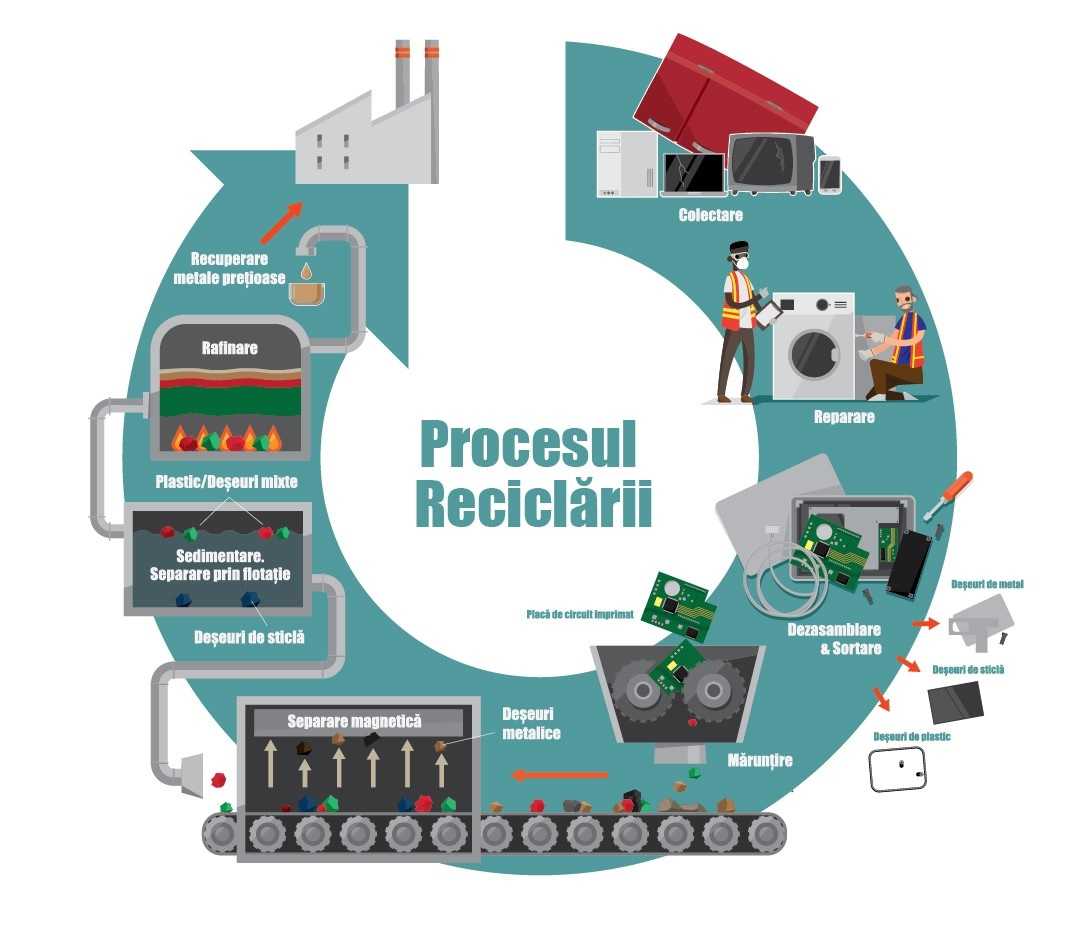
WHAT IS THE WEEE FLOW?
WHAT HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCES CONTAIN WASTE?
HOW DOES IT AFFECT THE PLANET AND PEOPLE'S HEALTH?
More details can be found here:
Freon:
CFC, HFC, HCFC; we find them in refrigeration equipment (including insulating foam) and in the insulating foam of boilers.
Harmful effects:
- degrades the ozone layer
- they have a high global warming potential, which will cause sea levels to rise, extreme weather events, melting glaciers, the extinction of many species and changes in human health.
Brominated flame retardants
Brominated flame retardants, which are found in both electronic boards and plastic cases, they don't degrade in the environment.
Harmful effects:
- Long-term exposure to these substances can lead to memory problems.
- They can also interfere with the normal functioning of the thyroid gland and the human hormonal system.
PCB - polychlorinated biphenyl compounds
Capacitors with PCB - polychlorinated biphenyl compounds. Found in older appliances, manufactured until 1987: washing machines, refrigeration equipment, dishwashers, hoods, dryers, microwave ovens, ballast for fluorescent lighting, lamps, copying equipment, power supplies, screens .
Harmful effects:
- PCBs are toxic to aquatic organisms and are lethal to high doses.
- PCBs affect the immune system and the reproductive system of various wild mammals.
- On humans, PCB exposure disrupts the normal functioning of the liver, immune system, genital tract, digestive tract, thyroid gland, bone marrow and gastric mucosa, behavioral disorders, thymus and lymph node atrophy.
PVC
Chlorine-containing plastic, reused in some electronics and for insulating cables.
Harmful effects:
- Improper processing (by burning) causes emissions of dioxins and furans that are very persistent in the environment and are the most toxic substances after radioactive materials, with effects such as: cancer, hormonal disorders, effects on the immune system, diabetes, learning difficulties, lungs and skin, chronic fatigue syndrome, hematological disorders, nervous system disorders and others.
Mercury
It is used in energy-saving lamps and bulbs, in LCD backlight lamps, but we also find it in batteries and old appliances, in switches and relays.
The UN has signed a new treaty under which more than 140 countries have agreed to ban a variety of mercury-containing products from the 2020 world market.
These include thermometers, batteries, with the exception of those used in medical devices used in implants, certain types of fluorescent lamps or cosmetics.
Harmful effects:
- Mercury affects the nervous system and kidneys
WHAT RAW MATERIALS ARE RECOVERED FROM WASTE?
Following the treatment of WEEE, are recovered secondary raw materials with economic value: iron, aluminum, copper, plastic and glass.
Electronic plates contain high value compounds - gold, silver, platinum, as well as rare metals: antimony, berylium, indium, gallium, etc.
There are also elements that after treatment do not have the quality of "recyclable", but they do have energetic value and can be co-incinerated in thermal power plants or in the cement industry: wood, plastic, rubber, etc.

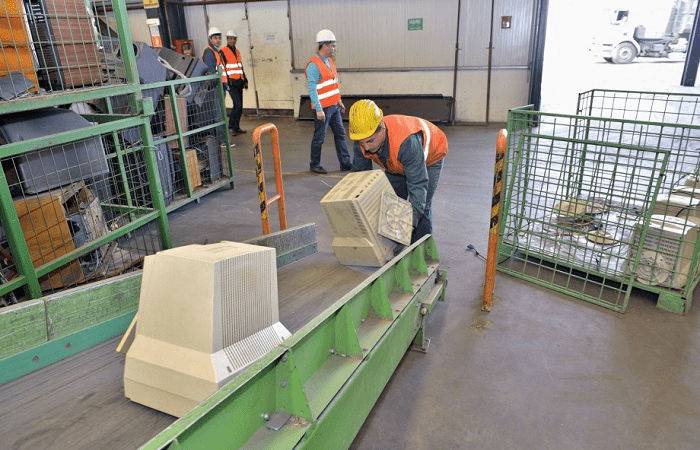
HOW ARE WASTE TREATED AND RECYCLED?

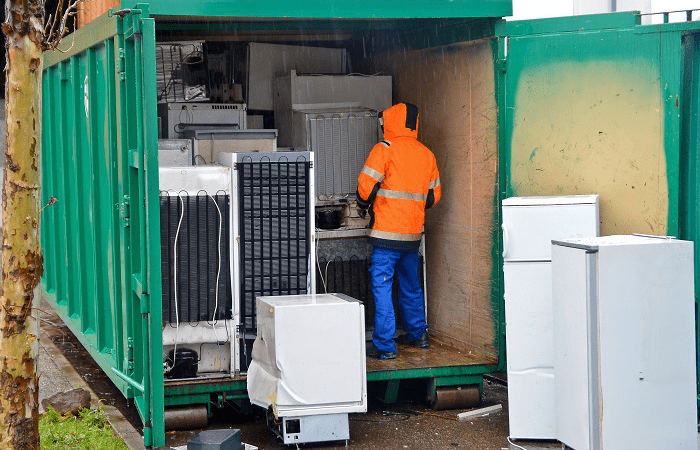
WEEE treatment involves initial sorting by type (refrigerators, CRT equipment, large appliances, IT, etc.)
- A first step is the extraction of components with high danger or that require careful treatment in the following flows: liquids, refrigerants, batteries, electronic boards, cables, asbestos, etc.
- Depolluted WEEE is to go through an automatic or manual dismantling process, at the end of which homogeneous compounds are identified and which form the basis for future secondary raw materials or which require energy recovery or controlled disposal operations.
Particular attention shall be paid to refrigeration equipment containing elements that affect the ozone layer and to cathode ray tube equipment that contains a fine powder with toxic elements inside.
WASTE REUSE
Certain types of WEEE, especially in the IT area - computers, servers, laptops - can be reconditioned and then reused. In Romania there are large areas with a real need for access to computers and the Internet. In the country side, in the disadvantaged communities, schools, orphanages, libraries or NGOs are really helped by receiving refurbished computers.
ECOTIC collaborates with Ateliere fără Frontiere, a leading NGO in implementing solutions for a social, solidarity and circular economy. Through an insertion workshop for people with social problems, AFF reconditions computers, equips them with authorized software and, quarterly, following a session of reception and selection of relevant projects, donates them to NGOs or institutions that carry out self-help activities of disadvantaged communities.
We are proud that over 2500 refurbished computers are now in schools, orphanages, social homes and social work organizations.

WEEELABEX STANDARD

WEEELABEX is an acronym derived from the expression "WEEE label of excellence", giving the name of the Project co-financed by LIFE - the European Community's environmental program (LIFE07 ENV / B / 000041). The project has a budget of € 1.064.600.
WEEELABEX is a project led by WEEE Forum in cooperation with stakeholders from the manufacturing community and industry (Digital Europe, CECED, EERA, ELC). This Project was created in 2009, and the creation of the WEEELABEX Organization, on April 17, 2013 in Prague, is considered the culmination of the project.
WEEELABEX's website is http://www.weeelabex.org. ECOTIC is a founding member of WEEELABEX.
It is a standard that defines clear requirements in operations in WEEE flows. It aims to limit pollution in WEEE collection-recycling operations, to ensure the safety and health of the people involved and to increase efficiency in the recovery of materials resulting from recycling processes. Its purpose is also to prevent the improper disposal of WEEE and their fractions, to limit illegal exports and to create a fair competitive environment for all actors in the WEEE chain.
EEA CLASSIFICATION
1. Heat transfer equipment;
2. Screens, monitors and equipment containing screens with an area of more than 100 cm2;
3. Lamps;
4. Large equipment, having any of the external dimensions greater than 50 cm;
5. Small equipment (no external size greater than 50 cm);
6. Small computer and telecommunications equipment, no external size greater than 50 cm
More details at Annex 2
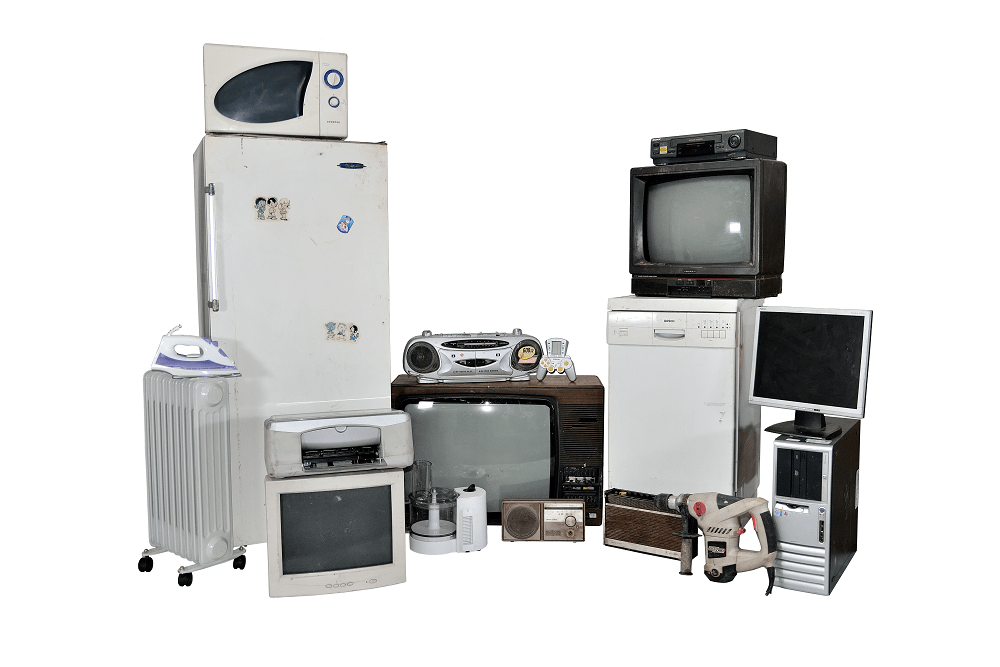

WASTE FRAMEWORK FROM THE POINT OF VIEW OF THE WASTE CODES FROM GD 856/2002

| 16 02 | Waste electrical and electronic equipment |
| 16 02 11 * | Discarded equipment containing chlorofluorocarbons, HCFCs, HFCs |
| 16 02 13 * | Discarded equipment containing dangerous components * 2) other than those specified in 16 02 09 to 16 02 12 |
| 16 02 14 | Discarded equipment, other than that specified in 16 02 09 to 16 02 13 |